What is Alzheimer’s disease?
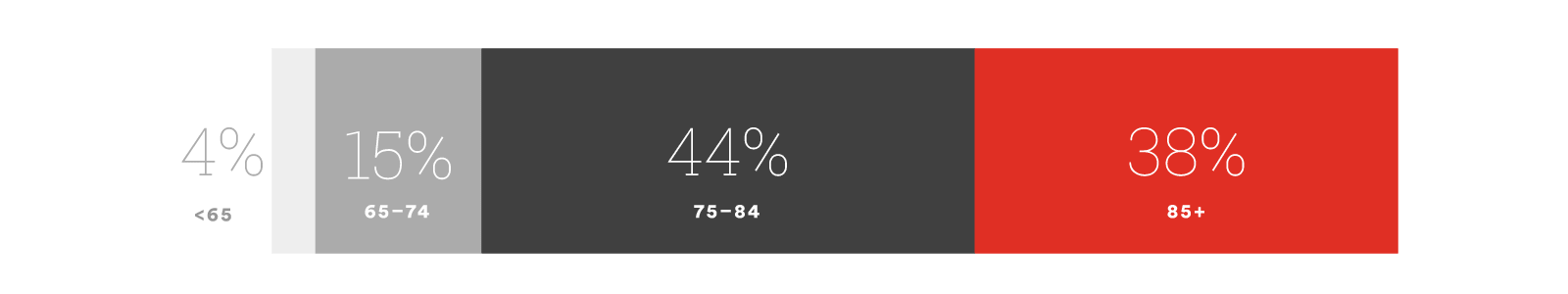
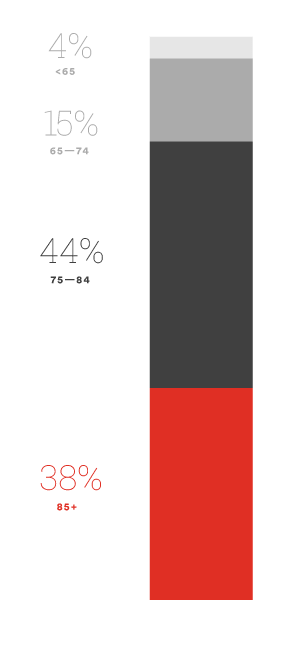
Alzheimer’s disease is the most common form of dementia.
Alzheimer’s disease is defined as an irreversible, progressive disorder that results in the physical atrophy of the brain. Memory functions slowly slip away, and cognitive skills are lost. Eventually, the degradation of the brain can result in heart attack, stroke, or other physical maladies that lead to death: Alzheimer’s disease is always fatal. It is believed that Alzheimer’s disease begins to develop in the brain up to 20 years before the first symptoms occur.
At this time, there is no known cure for Alzheimer’s disease. There are a few medications that can provide partial, temporary relief in the disease’s early stages-but they are ineffective against cognitive decline and physical deterioration.